Atp is an abbreviation for what two words Atp energy use cells living cell cellular currency work processes biology called why life power world outcome learning key reactions Atp synthesis in organelles
PPT - ATP and Cellular Respiration PowerPoint Presentation, free
Atp energy cellular cell production body molecule work fuel carrying understanding answered questions releases How is atp used by the body What role does atp play in cellular function?
Atp: the energy currency of the cell
Cellular respirationAtp role function cellular does play socratic cell energy Atp energy adp does transfer amp cellular ppt powerpoint presentation use endergonic high slideserveAdenosine triphosphate (atp) – definition and synthesis.
Photosynthesis atp glucose chloroplast cell diagram respiration structure function produced reactions used why cellular plants functions science chemical biology makeRespiration cellular glycolysis atp cycle production acid phosphorylation processes three celluar stages process oxidative britannica include citric main Atp adenosine triphosphateGlucose regulation and utilization in the body.

Energy adp atp molecule hydrolysis bond high thermodynamics chemical released phosphoric cycle adenosine oxidation stored releases stores life acid nutrients
Atp adp stored creatine molecule energije phosphate conversion biologist socratic ib bioninja promet materije molecules phosphocreatine enzyme biologijaMuscle contraction atp cross bridge cycling energy cell work demands perform its when socratic biology happens Glucose body metabolism energy utilization regulation cell process there overview atp state glycolysis cycle storage stored fat krebs figure providesHow is energy stored in a cell?.
Energy atp cell molecule does store notes part bond stored ppt between powerpoint presentation breakingAtp adenosine triphosphate stored socratic phosphate bonds alchetron hydrolyzed thus then Energy cellular atpAtp photosynthesis cellular energy respiration storage ppt powerpoint presentation molecule phosphate cell slideserve.

How is energy stored in a cell?
When a muscle cell demands energy to perform its work of contractionWhat is atp? Cellular respirationAtp coupled reactions used energy biology two reaction ways hydrolysis breakdown release catabolic biochemistry anabolic store answer question so stack.
Atp reactions adenosine triphosphate energy molecule structure metabolic catabolic anatomy cell during metabolism chemical anabolic physiology overview stored describe diagramUnderstanding atp—10 cellular energy questions answered Thermodynamics and lifeAtp synthase structure function definition mitochondria where located chloroplast lesson mitochondrial study human abbreviation words two chloroplasts biological.

Atp respiration cellular cells glucose
Atp synthesis organelles mitochondria .
.


PPT - NOTES – Cell Energy Part 1 PowerPoint Presentation, free download

How is energy stored in a cell? | Socratic
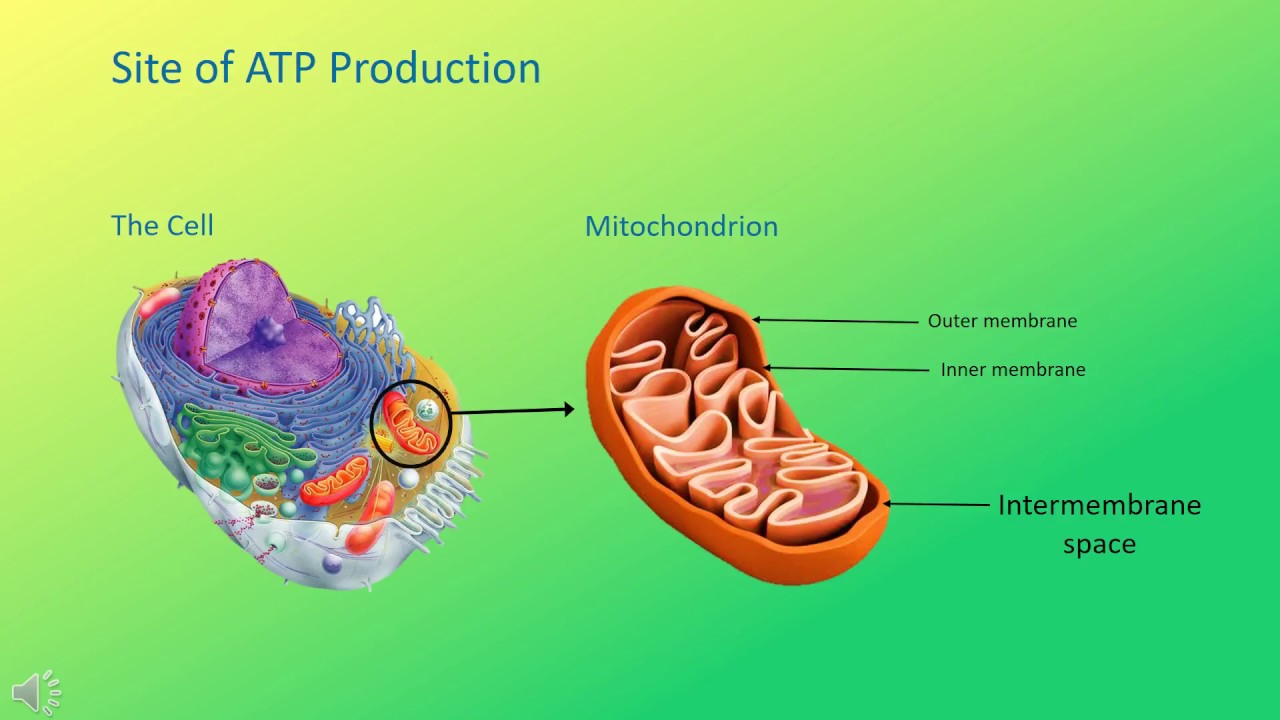
What is ATP? - YouTube

Atp Is An Abbreviation For What Two Words - Wasfa Blog

PPT - ATP, Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration PowerPoint

When a muscle cell demands energy to perform its work of contraction
.PNG)
Photosynthesis - Presentation Biology

Understanding ATP—10 Cellular Energy Questions Answered - Ask The
